
caisson
technology
technology
harbor technology
/green technology



- Mud pressurization (DK) shield method
- Double-O-Tube (DOT) shield method
- Developing Parallel Link Excavation (DPLEX) shield method
- Jack-driven Developing Parallel Link Excavation (J-DPLEX) shield method
- Detaching And Proceeding to dig Piping (DAPPI) construction method
- Mud pressurizing propulsion method




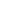
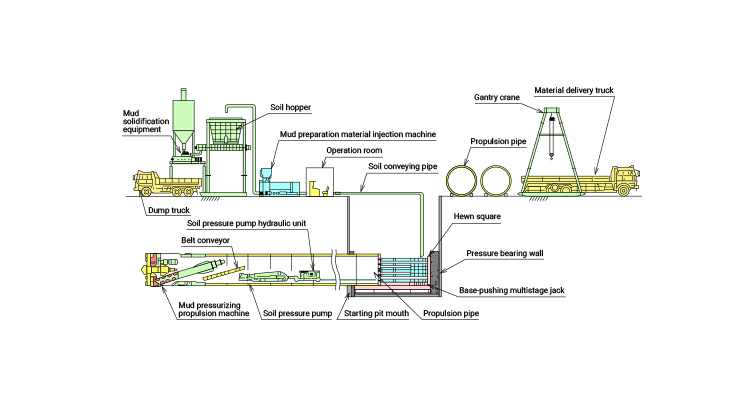
Civil Engineering Business: Mud Pressurization Propulsion Method
The representative construction method of the earth pressure propulsion method
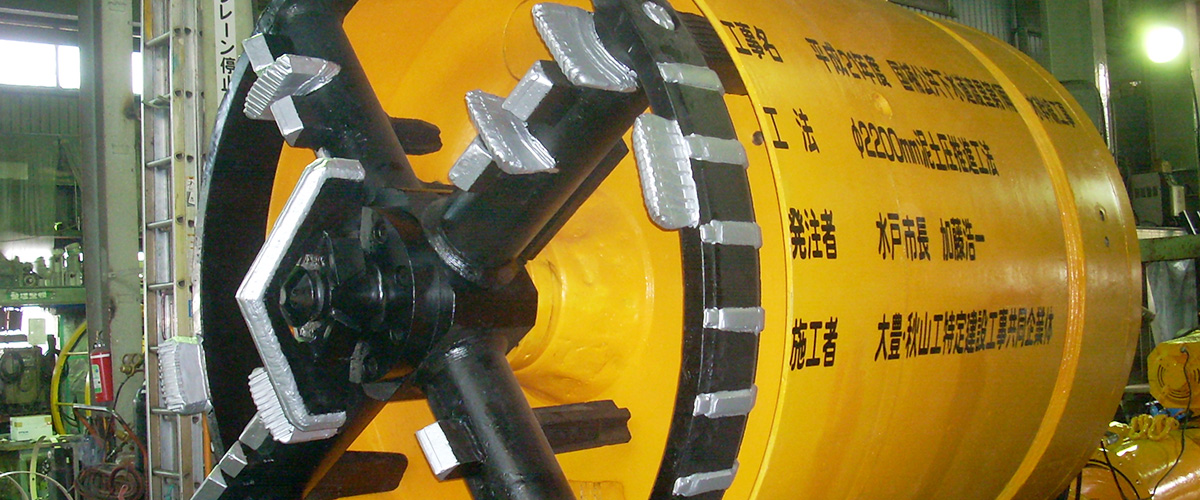


Outline of the construction method
The mud pressurization propulsion method is a representative method of the mud pressure propulsion method classified as the earth pressure propulsion method. This method can be widely applied to complicated soil conditions, and it is a method superior in stability, safety, and economic efficiency of cut faces even under the difficult conditions of a small overburden zone, long distance, and curved line propulsion.
Applicable soil property: Sand layer, sand gravel layer, boulders, cobblestone layer, silt clay layer, and white sand layer. Pipe type: Reinforced concrete pipe, ductile cast-iron pipe, and other pipe. Pipe diameter: Nominal diameter φ800 mm to φ3,000 mm Propulsion distance: Approx. 1,000 m at maximum Special use: Has been used in many river, railway, and road intersection projects in small overburden zones. Usable for work in sharp curved lines.
Characteristics of the construction
method
By adjusting the concentration and amount of mud control agent for the sand layer, sand gravel layer, silt clay layer, white sand layer, and alternate layers as necessary, they can be converted into mud having a plastic flow capability and impermeability, which can be applied to a wide range of soil properties. Maximum gravel diameter: Applicable to propulsion work of large gravel layer of approximately φ500 mm.
The discharged remaining soil can be transported using a belt conveyor, mortar box, and soil pressure pump without requiring large-sized treatment equipment for processing the remaining soil.
Since the cut face can be completely suppressed by mud, the ground hardly changes, making it possible to minimize the sinking of the ground surface. It has been used for small overburden zones of below 0.5 D and propelling under an existing box at 0.6 m elongation.
There is no need for an auxiliary construction method, in principle, except for the initiating/reaching point of the propulsion machine, sharp curved-lines, and neighboring work area.
There is no need for large plant equipment, and work can be performed with a minimum shaft area. It is therefore ideal for work in urban areas.
Curved lines can be easily processed by considering the length of propulsion machine and joint clearances.
This method has been used for super-long distance propulsion work with φ1,600 mm nominal diameter and a single span of 967 m.
(External diameter of propulsion machine φ1,820 mm: Ductile cast-iron pipe)
Mud Pressurization Propulsion
Method Association
This study group has been established in 1988 to improve and disseminate the technology of the method and consists of 22 companies as regular members and 3 companies as supporting members.
To the web site