
caisson
technology
technology
harbor technology
/green technology



- Mud pressurization (DK) shield method
- Double-O-Tube (DOT) shield method
- Developing Parallel Link Excavation (DPLEX) shield method
- Jack-driven Developing Parallel Link Excavation (J-DPLEX) shield method
- Detaching And Proceeding to dig Piping (DAPPI) construction method
- Mud pressurizing propulsion method




Outline of pneumatic caisson
This construction method sinks caisson through excavation using air pressure.


Outline of Pneumatic Caisson
Construction Method
The pneumatic caisson method builds caissons made of reinforced concrete having a workroom where excavation is conducted, eliminates groundwater by sending compressed air matching the groundwater pressure to the workroom in order to perform excavation/sinking constantly in a dry environment, and installs the structure at the predetermined location. This construction method is widely used for underground structures including foundation of bridge, shield work shafts, and the foundation of the dam.
Procedure of Pneumatic Caisson
Construction Method
As for the work procedure, construction, excavation, and sinking is repeatedly conducted for each lot, and after ground support is confirmed, hollow-filling concrete is charged in the workroom in a dry environment.

Principle of Pneumatic
Caisson
Construction Method
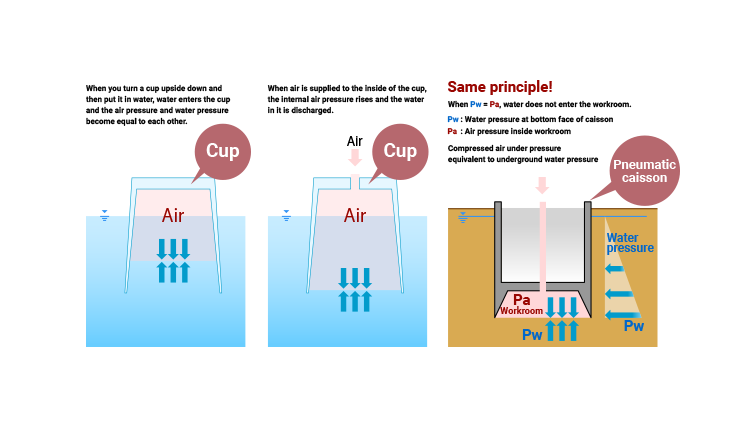
The pneumatic caisson method is an application of the principle that a cup turned upside down can prevent entry of water due to air pressure when it is pushed into water in a flat state. In fact, an airtight workroom is built in the lower area of the caisson, and by sending compressed air into it, entry of groundwater is prevented, allowing for excavation in a dry state. The inside of the cup corresponds to the caisson workroom, and the tip of the cup corresponds to the blade tip of the caisson.
Characteristics of Pneumatic
Caisson Construction Method
Bridge foundations and structures built using the pneumatic caisson method have many superior characteristics.
- Highly reliable as a structure
- Durable
- Applicable to various soil properties from soft ground to rocks
- Secure process management
- Existing structure/foundation or unexpected underground obstacles can be securely removed
- Less impact on the surrounding environment
- Suitable for neighboring work
- Economical in terms of total cost
Comparison of Pneumatic
Caisson Foundation and
Other Construction Methods
|
Construction
method Construction
condition |
Pneumatic caisson | Open caisson | Steel pipe sheet pile well |
Continuous under ground wall |
Ready-made pile | Cast-in-place pile | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Driving | Pile press-fitting by inner excavation | |||||||
| Construction depth |
5 to 15m | |||||||
| 15 to 25m | ||||||||
| 25 to 40m | ||||||||
| 40 to 50m | ||||||||
| 50 to 60m | ||||||||
| 60 to 70m | ||||||||
| Soil quality |
Soft soil | |||||||
| Hard soil | ||||||||
| Base/ cobblestone |
||||||||
| Rock | ||||||||
| Removal of obstacles |
||||||||
| Check of bearing layer |
||||||||
| Underground water |
Pressurized groundwater | |||||||
| Flowing groundwater (flowrate of approx. 3 m/min or higher) | ||||||||
| Reliability | Resistance against earthquake |
|||||||
| Durability | ||||||||
| Workability | Work above water | |||||||
| Space with narrow work area |
||||||||
| Work under floor | ||||||||
| Environment | Measures against noise/vibration | |||||||
| Influence on adjacent structures |
||||||||
| Utilization of underground space | ||||||||
Our Works
-
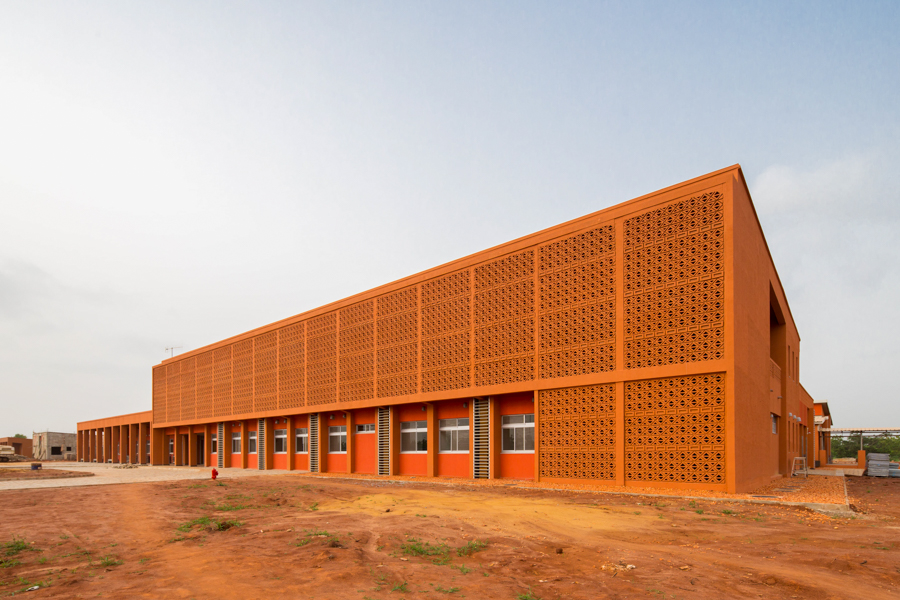

- Facility name
- The Project of Construction and Equipment for Alada Hospital in Atlantic state
- Construction site
- Republic of Benin
- Client
- Ministry of Health, the Repablic of Benin
-
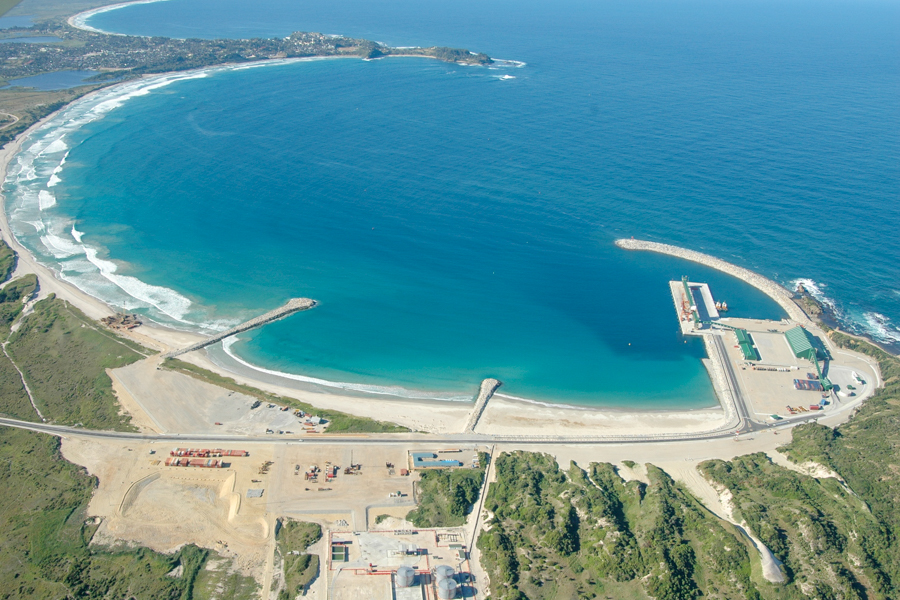

- Facility name
- Construction work for Port of Ehoala
- Construction site
- Republic of Madagascar
- Client
- PORT d’EHOALA S.A.
-
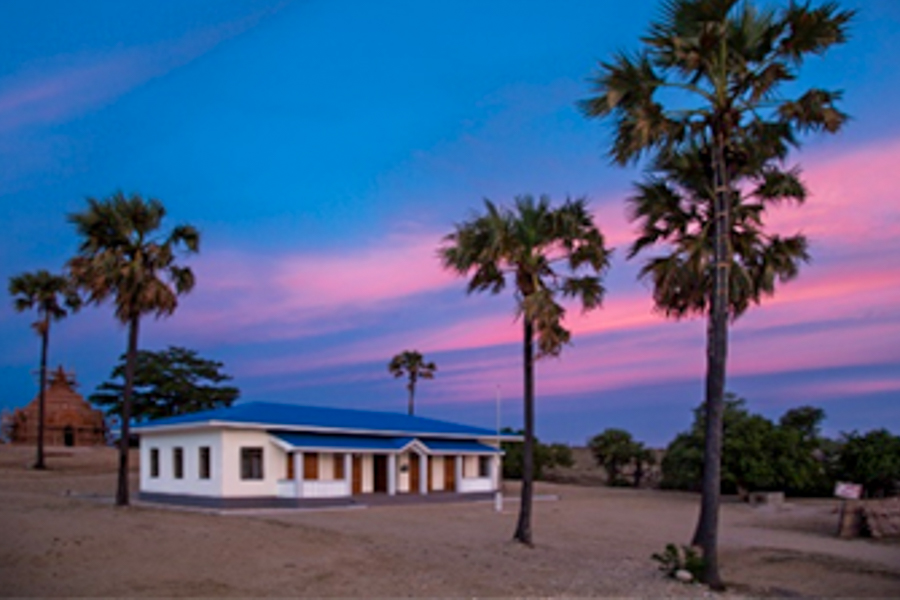

- Facility name
- Construction Works for the Project for Upgrading the Health Facilities in Central Myanmar
- Construction site
- Republic of the Union of Myanmar
- Client
- Ministry of Health