
caisson
technology
technology
harbor technology
/green technology



- Mud pressurization (DK) shield method
- Double-O-Tube (DOT) shield method
- Developing Parallel Link Excavation (DPLEX) shield method
- Jack-driven Developing Parallel Link Excavation (J-DPLEX) shield method
- Detaching And Proceeding to dig Piping (DAPPI) construction method
- Mud pressurizing propulsion method




Civil Engineering Business: Dredged Soil-sand Recycling (DRES) Construction Method
The construction method for reducing dredged soil volume and recycling
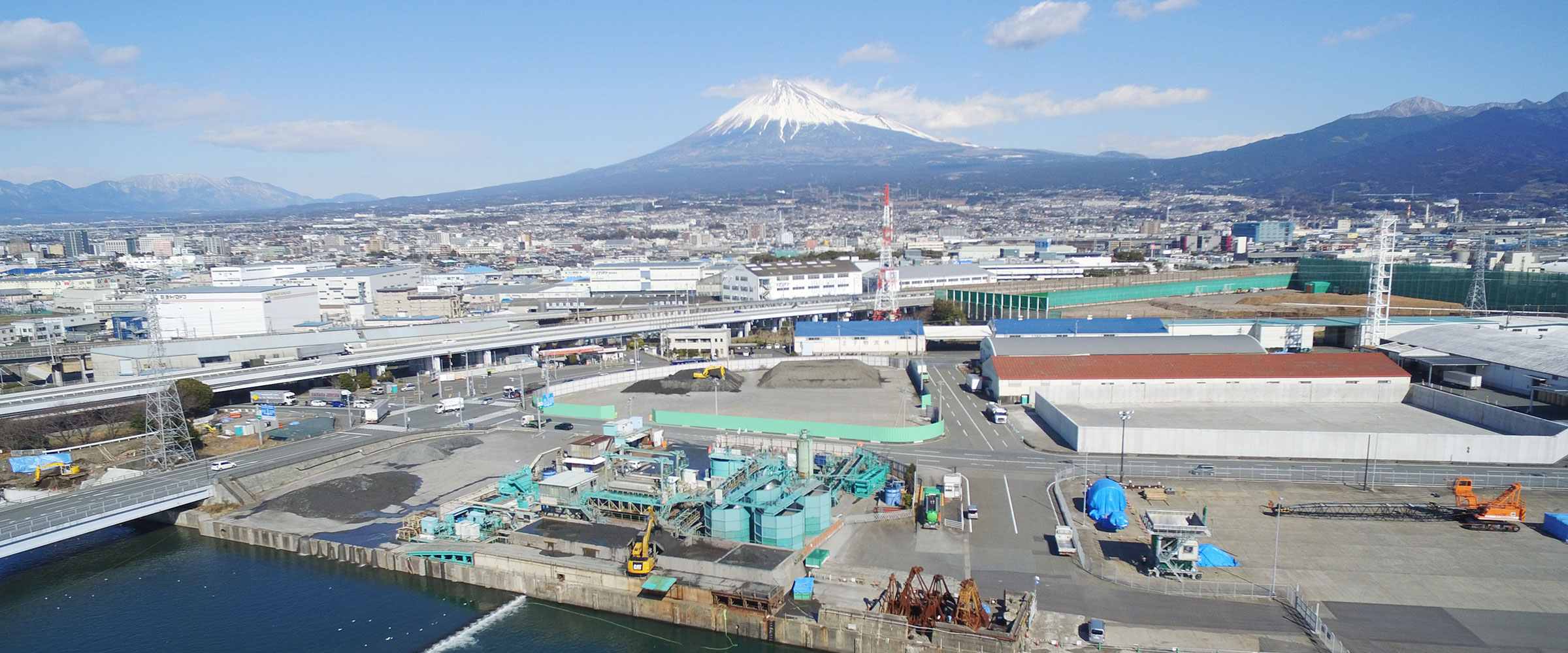


Outline of the
construction method
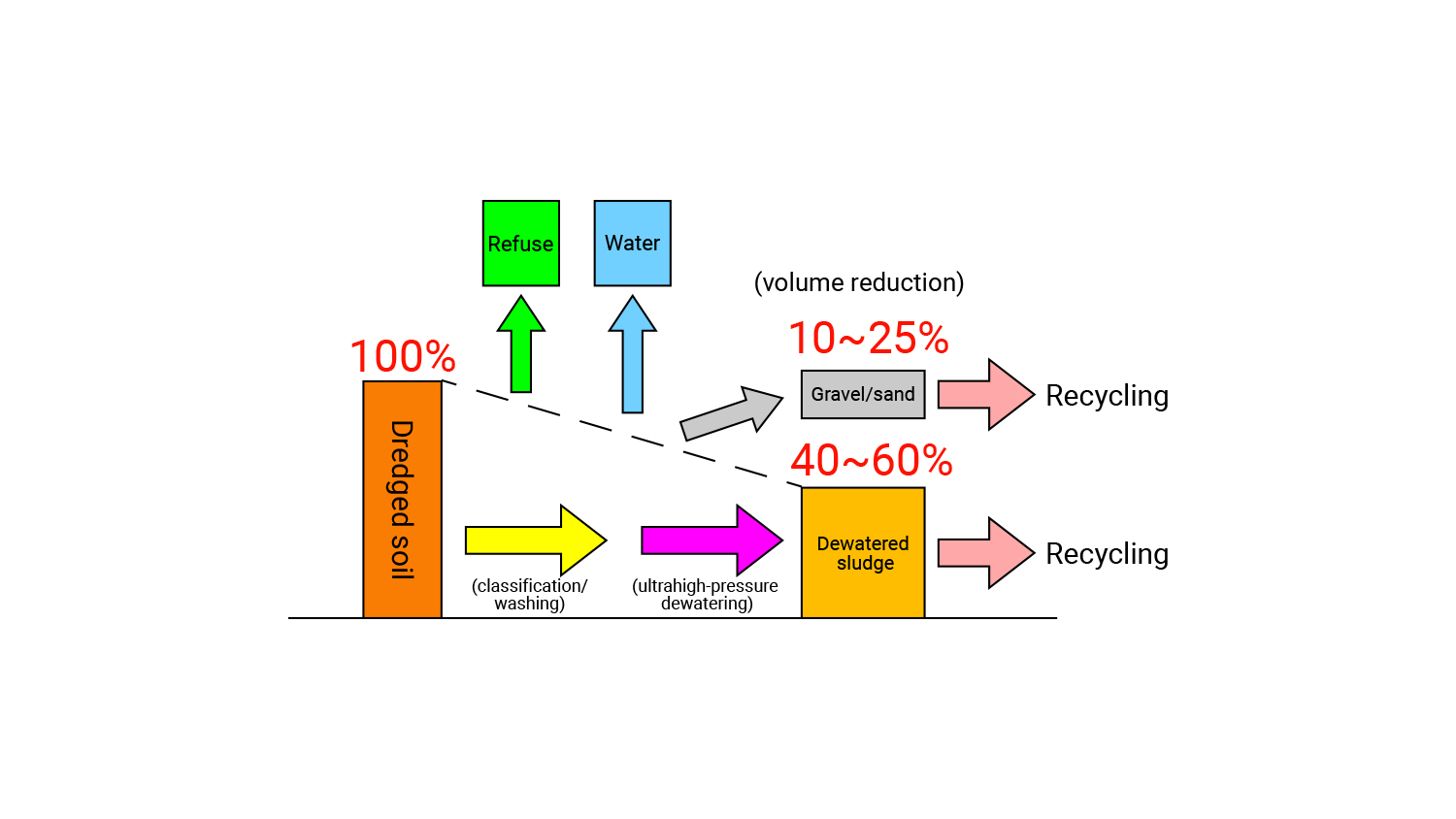
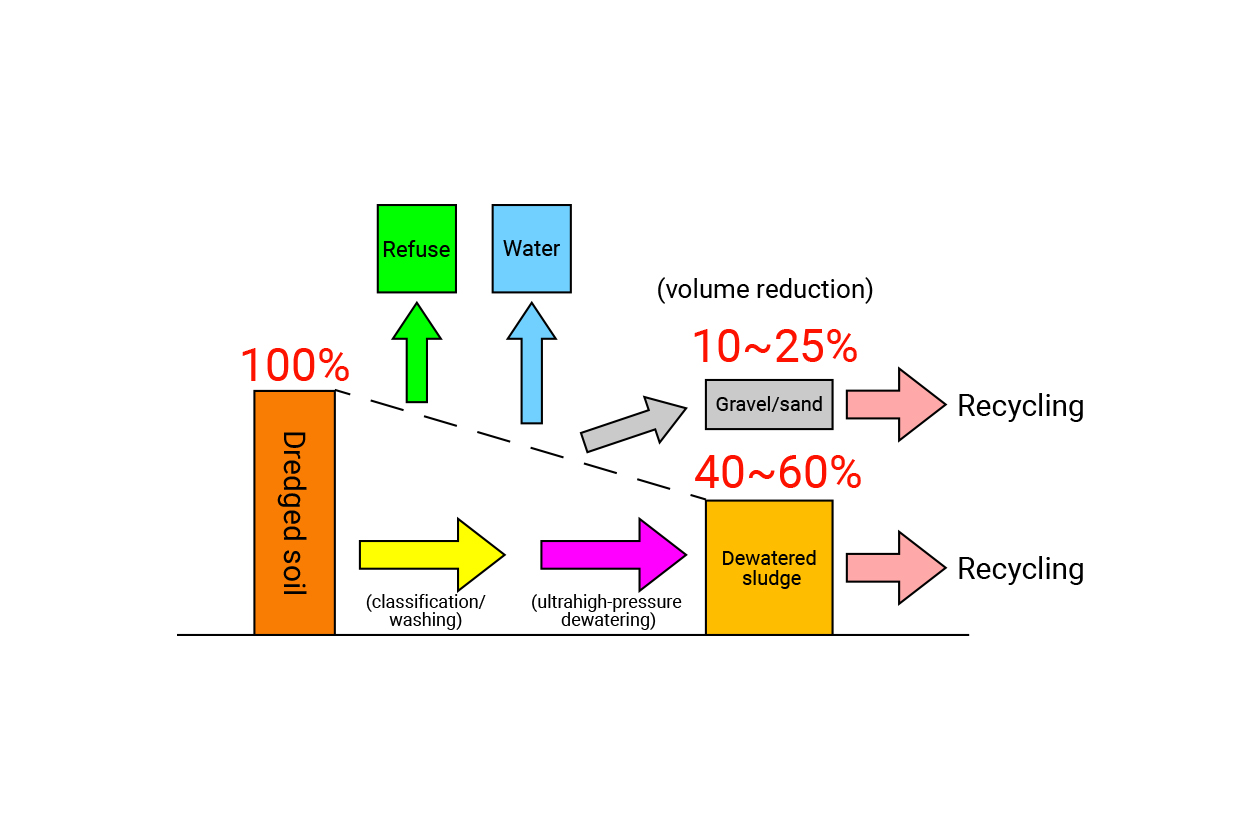
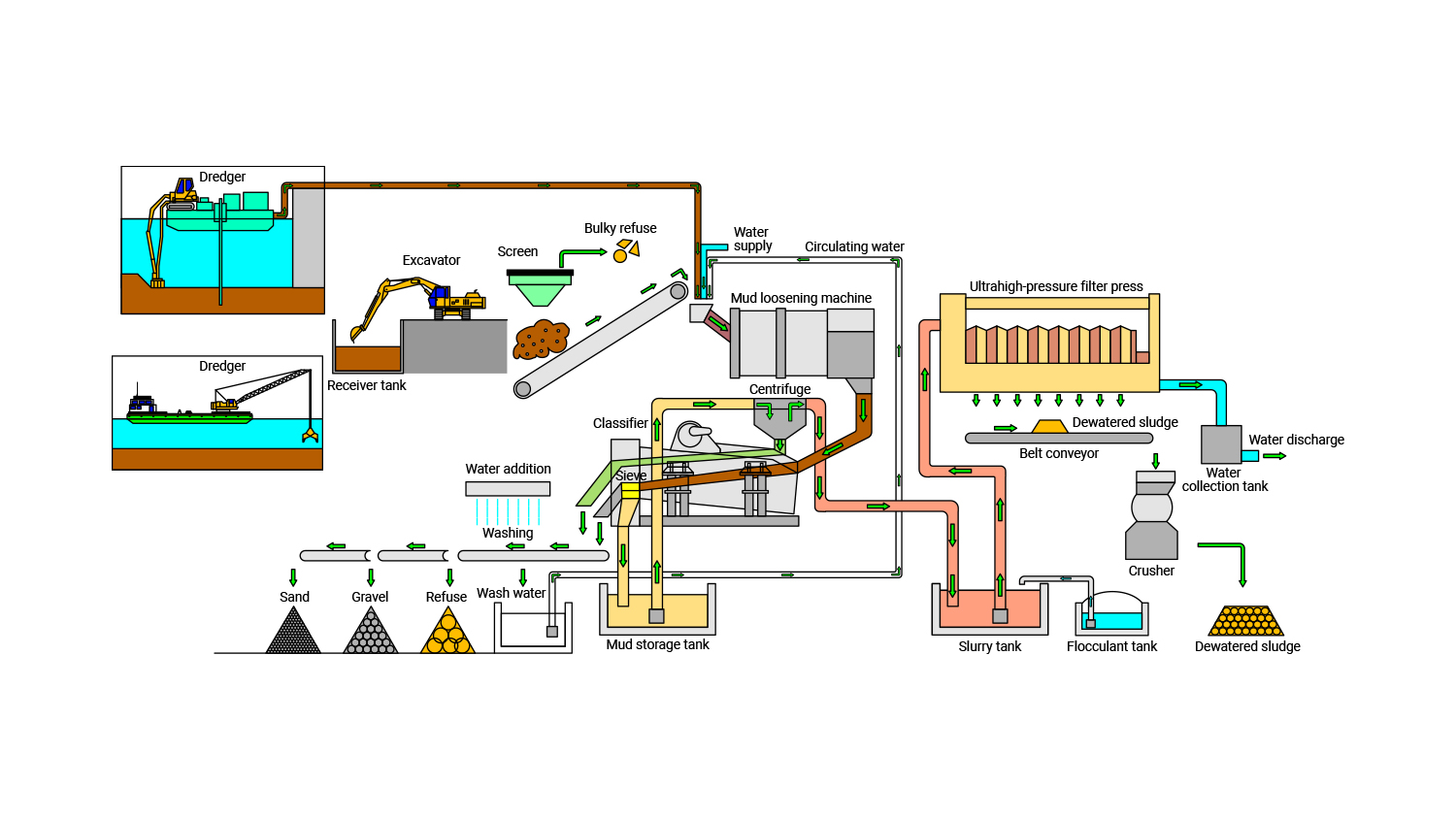
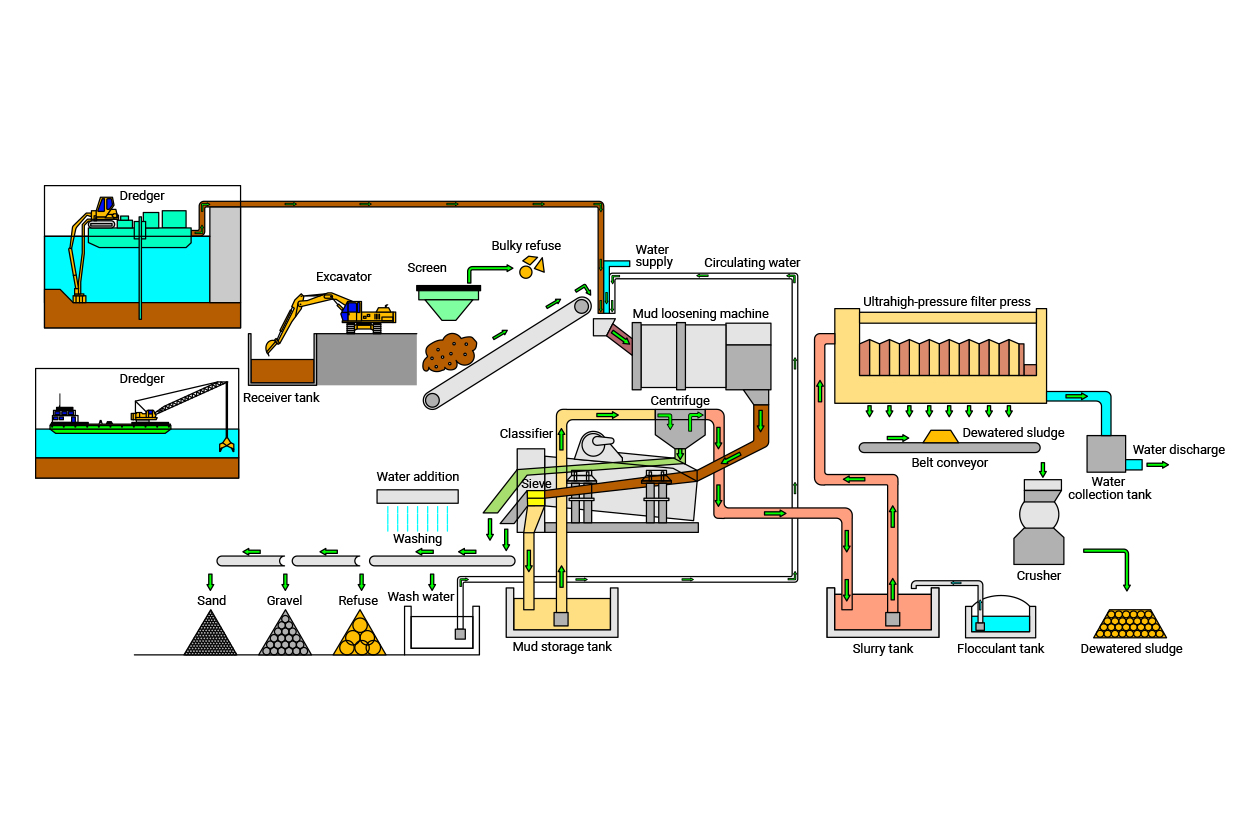
The DRES construction method (dredged soil-sand recycling method) identifies gravel and sand contained in the dredged soil and treats remaining mud water with high water content as second class treated soil of cone index >800 kN/m2, thereby making it possible to reduce a large amount of dredged soil and recycle it.The DRES construction method (dredged soil-sand recycling method) identifies gravel and sand contained in the dredged soil and treats remaining mud water with high water content as second class treated soil of cone index >800 kN/m2, thereby making it possible to reduce a large amount of dredged soil and recycle it. This system is developed by combining a mud loosening machine that converts dredged soil into homogeneous slurry, a classifier that segregates gravel and sand, a filter press that dewaters silt clay at 4 MPa at ultrahigh pressure, and a crusher that crushes dewatered sludge. This method has been used not only for dredged soil in ports and harbors but also for purifying rivers and ponds. (Patent: No. 4364889 and others)
Characteristics of the
construction method
The gravel and sand discharged in the treatment process are reused as building materials, and dewatered sludge is utilized as subgrade material or banking material.
This method can also be used to treat mud water in ponds and rivers at low concentration in addition to dredged soil in ports and harbors.
Conceptual diagram
of the system
The crushing device crushes and adjusts the shape of particles of the gravel and dust mixed into the dredged soil, and the separator separates dust, gravel, sand, and slurry (liquefied fine soil). The separated gravel and sand are reused for building materials. Slurry (liquefied fine soil) is dewatered and solidified by a high-pressure filter press to be utilized for subgrade material, banking material, and other material.