
caisson
technology
technology
harbor technology
/green technology



- Mud pressurization (DK) shield method
- Double-O-Tube (DOT) shield method
- Developing Parallel Link Excavation (DPLEX) shield method
- Jack-driven Developing Parallel Link Excavation (J-DPLEX) shield method
- Detaching And Proceeding to dig Piping (DAPPI) construction method
- Mud pressurizing propulsion method




Technology and process of pneumatic caisson
The technology and process of pneumatic caisson is introduced.
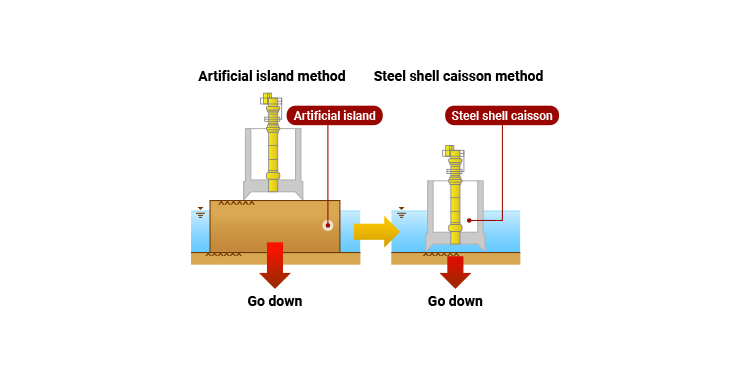
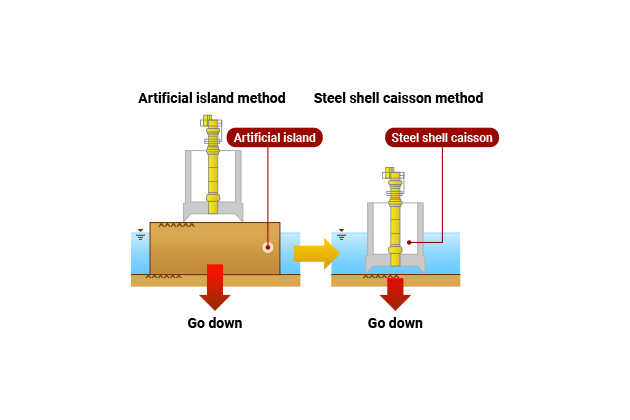
Steel shell caisson (floating shoes) Construction method
In 1957, as a new construction method replacing the Artificial island method, we adopted the Steel shell caisson (called “ukigutsu (floating shoes)” at that time) for the lock gate of Hachisawaura harbor in Fukushima Prefecture for the first time in Japan. It eliminates the need for shuttering and artificial islands, thus this method is economical and can reduce the blocking rate of cross-sectional surfaces of rivers.
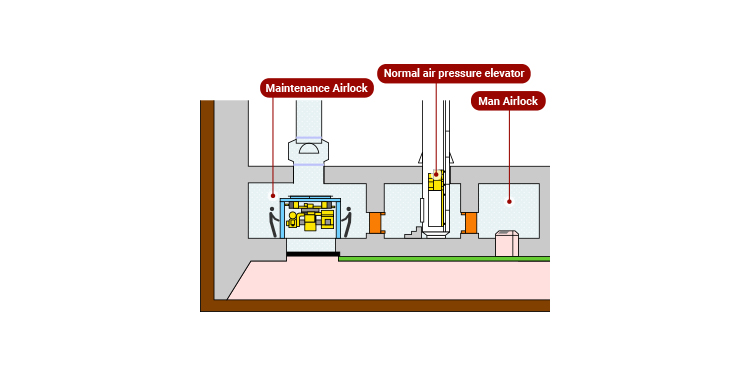
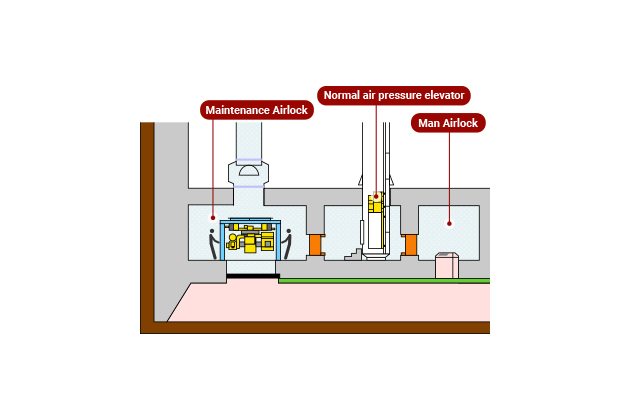
Development of normal air
pressure elevator using double
slabs.
When operators ascend/descend by using spiral staircases of man shaft, it places a greater burden on the body as they go deeper, and it can trigger decompression sickness. By adopting a double-slab structure, we installed a man lock straight above the workroom so people can ascend and descend in between by using a normal pressure elevator. It is extremely effective in improving the environment of ascending/descending work and preventing decompression sickness. (Patent: No.3349974 filed on Dec 28,1998 and others)
DREAM construction method
(unmanned excavation method
using remote operation system)
Since around 1965, many attempts have been made for mechanizing excavation using pneumatic caissons, and in 1987, we initiated development of unmanned excavation construction method using a full-scale remote operation system. Subsequently, in 1988, we obtained successful results through the demonstration experiment conducted with the Asagano River Bridge (substructure) in Tohoku Odan Expressway and established the DREAM construction method (unmanned excavation construction method). DREAM is an abbreviation of Daiho Remote control Excavation Automatic Method. (Patent: No.1795378 filed on Dec 28,1998)
-
 DREAM excavator
DREAM excavator -
 Remote operation system
Remote operation system
Multifunctional caisson excavator
DREAM II (unmanned excavator)
In 1997, we developed the multifunctional caisson excavator DREAM II, which is capable of handling a wide range of soil properties from impermeable layer to sand gravel layer and rocks and performing excavation through remote operation. It was adopted for the construction work of the Mabechi River Bridge on the Tohoku Jukan Expressway (substructure) and succeeded in excavating rocks. With this excavator, it is easy to attach a variety of different attachments, such as a rock drill (attachment is performed by human), breaker, and drum cutter in a short period in order to excavate and destroy rocks, boulders, and existing underground structures, in addition to the sand gravel and silt. It is a multifunctional overhead traveling caisson excavator. (Patent: No. 3794511 filed on Jul.5,1996)
-
 DREAM II excavator (bucket 0.3 m3)
DREAM II excavator (bucket 0.3 m3) -
 DREAM II excavator Breaker (300 kg class)
DREAM II excavator Breaker (300 kg class) -
 DREAM II excavator Drifter (350 kg class)
DREAM II excavator Drifter (350 kg class)
New DREAM construction method
(New Daiho’s pneumatic caisson
method)
The New DREAM construction method is a new pneumatic caisson method built with the concept of combining unmanned technology for work under high pressure and safety technology according to the work conditions.
Main equipment
The equipment used in the pneumatic caisson construction work is classified into excavation equipment, outfitting equipment, material removal equipment, and first aid equipment.
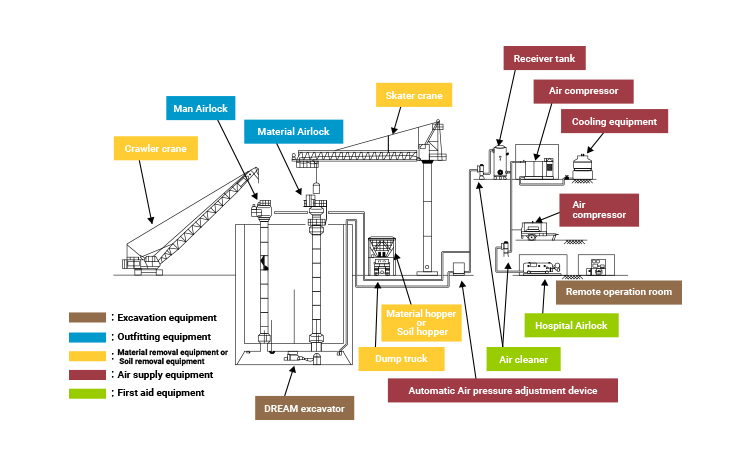
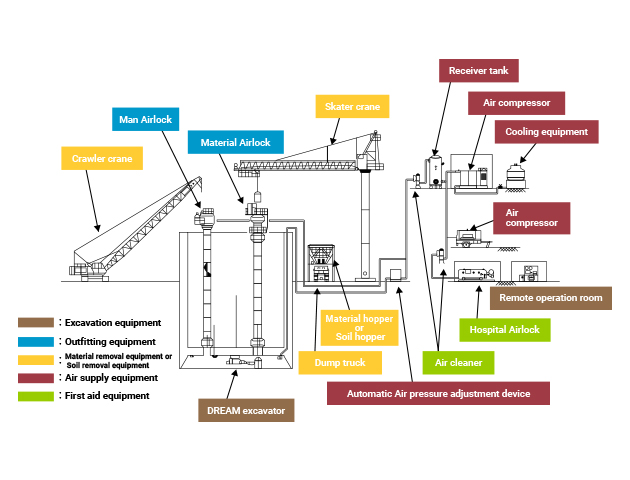
The equipment used in the pneumatic caisson construction work is classified into excavation equipment, outfitting equipment, material removal equipment, and first aid equipment.
| Motor output | Bucket capacity | Max work air pressure | Excavatable soil property | Machine weight | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DREAM II type excavator | 37Kw | 0.30m3 | 0.7MPa | Ordinary soil to hard rock | 6.4 t |
| DREAM III type excavator | 22Kw | 0.23m3 | 0.7MPa | Ordinary soil to hard rock | 4.3 t |
Equipment used in pneumatic caisson work